This is an injection into the vitreous, which is the jelly-like substance inside your eye. It is performed to place medicines inside the eye near the retina.
Intravitreal injections are used to deliver drugs to the retina and other structures in the back of the eye, thus avoiding effects on the rest of the body. Common conditions treated with intravitreal injections include diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, retinal vascular diseases and ocular inflammation.
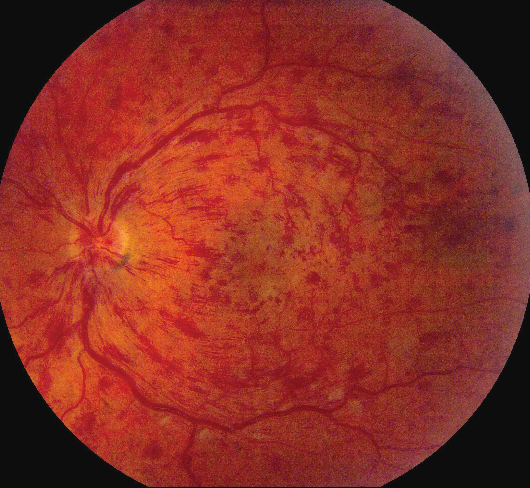
Ischemic central retinal vein occlusion(CRVO) with macular edema
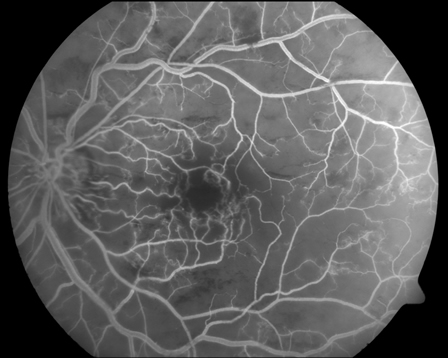
Fluorescein angiogram in ischemic CRVO
Procedure
Once your pupils are dilated, the actual procedure may take around 10 minutes and is carried out in minor operation theatre. You will be made to lie down in a comfortable position and anaesthetic (numbing) drops will be applied in your eye. Your eye will be cleaned with an iodine antiseptic solution. A speculum is inserted and the medicine injected into the vitreous. You may experience a mild discomfort during the procedure. Antibiotic ointment will be applied and the eye padded. Antibiotic eye drops need to be instilled for a week.
The doctor will see you the next day for inflammation or increase in intraocular pressure.
Instructions following an intravitreal injection
- There are no special precautions except to avoid rubbing the eye.
- Instill the antibiotic eyedrops 4 times a day for 1 week.
- You can also take mild painkillers to alleviate any discomfort during the first few days.
Normal effects following an intravitreal injection
- A subconjunctival haemorrhage (bloodshot eye) usually occurs at the injection site. This will gradually fade within 7 to 10 days..
- Your vision may become slightly more blurred immediately after the injection. There may also be some floaters in your vision.
- You may experience mild discomfort for a few days after the injection. This discomfort should be relieved by mild painkillers.
Warning symptoms following an intravitreal injection
Although rhegmatogenous retinal detachment and cataract are potential complications of intravitreal injection, the most feared complication is endophthalmitis i.e. infection inside the eye (rates typically less than 1%).
The warning symptoms of this complication are rapid onset of:
- Increasing eye pain.
- Increasing redness of the eye.
- Greatly decreased vision.
You must contact the hospital immediately for advice if you develop these warning symptoms. It is very important to identify and treat this type of infection as quickly as possible.
